The lower the ignition temperature, the more dangerous the substance. Consequently, materials are classified from T1 to T6 according to the maximum surface temperature (or temperature of the hottest point, depending on the protection).
Identification of substances
The dangerousness of an explosive atmosphere depends on its concentration of flammable substances, but also on the characteristics of these substances. It is necessary to divide these substances into two hazard classes:
gas and dust groups
self-ignition temperature (temperature classes for gases).
The lower the energy required to ignite a substance, the more dangerous it is.

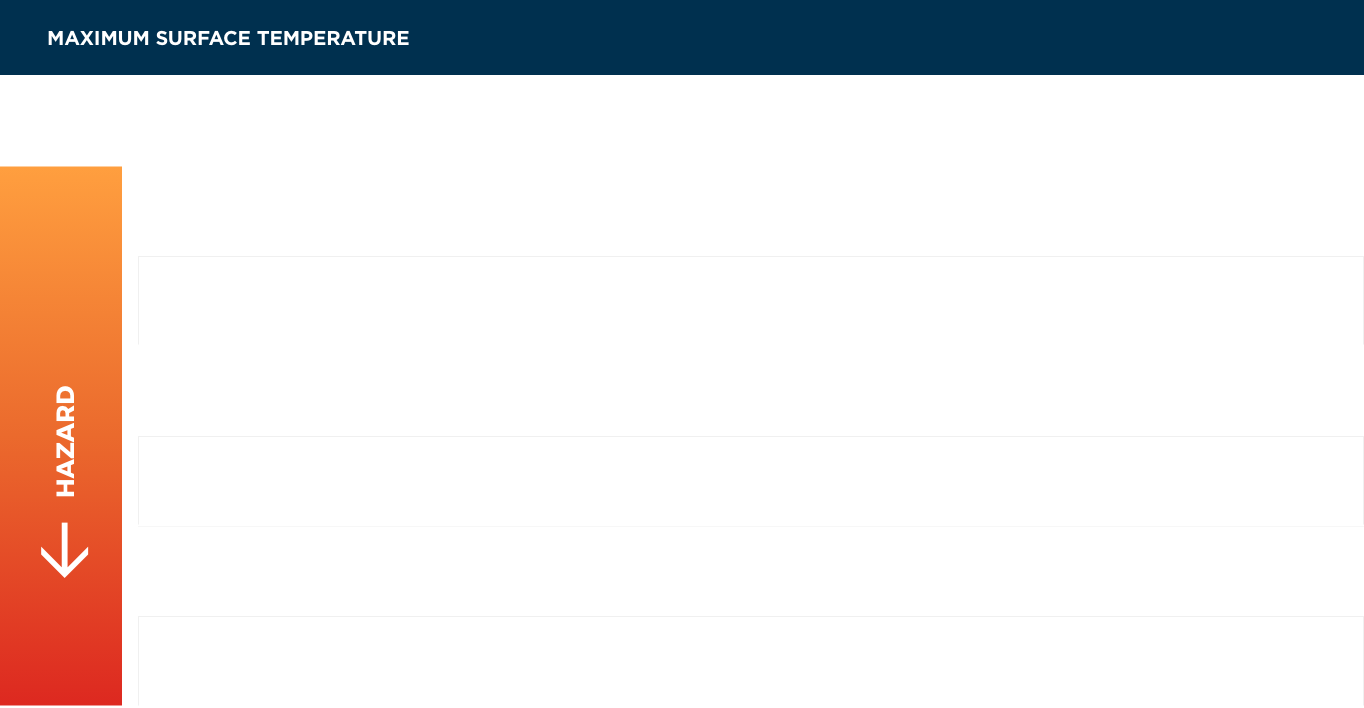
A device classified T6 is suitable for an atmosphere with an ignition temperature of T5, T4, T3, T2 or T1. Note: the ignition temperature of a gas is not related to its dangerousness. Even though hydrogen is an extremely explosive gas (the energy required to ignite it is around 10 times lower than for natural gas), it is only classified as T1, because its ignition temperature is very high (560°C).

PROTECTION SYSTEMS
The rules governing the design and verification of protection systems are governed by international standards, and the equipment is identified by letters.

Other types of protection exist: Protection of equipment and transmission systems using optical radiation (op pr, op is,…), ventilated rooms (v),… Non-electrical equipment can also create potential sources of ignition and to address this issue, there are protection modes for this type of equipment.


